Odoo is one of the most popular business softwares in the world. There are several ways to install Odoo depending on the required use case.
The easiest and quickest way to install Odoo is by using their official repositories.
If you want to have more control over versions and updates or if you want to run multiple Odoo versions on your machine then this approach will not work for you because the Odoo package doesn’t allow multiple Odoo installations on the same machine. In this case you can either use docker and docker compose or install Odoo in a Python virtual environment.
This guide covers the steps necessary for installing and configuring Odoo using Git source and Python virtual environment on Ubuntu 16.04.
Before you begin
Before continuing with this tutorial, make sure you are logged in as a user with sudo privileges .
Update the packages index and all installed packages to the latest packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstall Git , Pip , Node.js and the tools required to build Odoo dependencies:
sudo apt install git python3-pip build-essential python3-dev libxslt-dev libzip-dev libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev node-lessCreate Odoo user
Create a new system user and group with home directory /opt/odoo that will run the Odoo service:
useradd -m -d /opt/odoo -U -r -s /bin/bash odooInstall and configure PostgreSQL
Install the PostgreSQL package from the Ubuntu’s default repositories:
sudo apt install postgresqlOnce the installation is complete create a new PostgreSQL user with the same name as the previously created system user, in our case that is odoo:
sudo su - postgres -c "createuser -s odoo"Install Wkhtmltopdf
In order to print PDF reports, you will need the wkhtmltopdf tool. The recommended version of Wkhtmltopdf is 0.12.1 which is not available in the official Ubuntu 16.04 repositories. We’ll download and install the recommended version from the official Wkhtmltopdf site.
Download the package using the following wget command:
wget https://builds.wkhtmltopdf.org/0.12.1.3/wkhtmltox_0.12.1.3-1~xenial_amd64.debOnce the download is completed install the package by typing:
sudo apt install ./wkhtmltox_0.12.1.3-1~xenial_amd64.debInstall and configure Odoo
We will install Odoo from the GitHub repository in an isolated Python environment so we can have more control over versions and updates.
Before starting with the installation process, make sure you switch to user “odoo”:
sudo su - odooTo confirm that you are logged in as user odoo, use the following command:
whoamiStart with the installation process by cloning the Odoo source code from the GitHub repository:
git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 11.0 /opt/odoo/odoo11- If you want to download and install a different Odoo version just change the version number after the
--branchswitch. - You can download Odoo source code to any as you like, for example instead
odoo11you can use the name of your domain.
virtualenv is a tool to create isolated Python environments. To install it use:
pip3 install virtualenvCreate a new Python virtual environment for the Odoo installation with:
cd /opt/odoovirtualenv odoo11-venv
Activate the environment:
source odoo11-venv/bin/activateInstall all required Python modules:
pip3 install -r odoo11/requirements.txtBefore you begin section.Once the installation is completed deactivate the environment and switch back to your sudo user using the following commands:
deactivateexitIf you intend to install additional modules it is best to keep those modules in a separate directory. To create a new directory for the additional modules run:
sudo mkdir /opt/odoo/odoo11-custom-addonssudo chown odoo: /opt/odoo/odoo11-custom-addons
The next thing we need to do is to create a configuration file. We can either create a new one from scratch or copy the included configuration file:
sudo cp /opt/odoo/odoo11/debian/odoo.conf /etc/odoo11.confOpen the file and edit it as follows:
sudo nano /etc/odoo11.conf[options]
; This is the password that allows database operations:
admin_passwd = my_admin_passwd
db_host = False
db_port = False
db_user = odoo
db_password = False
addons_path = /opt/odoo/odoo11/addons
; If you are using custom modules
; addons_path = /opt/odoo/odoo11/addons,/opt/odoo/odoo11-custom-addons
Once you are done, close and save the file.
my_admin_passwd to something more secure and adjust the addons_path if you’re using custom modules.Create a systemd unit file
To run odoo as a service we need to create a odoo11.service unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory.
Open your text editor and paste the following lines:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo11.service[Unit]
Description=Odoo11
Requires=postgresql.service
After=network.target postgresql.service
[Service]
Type=simple
SyslogIdentifier=odoo11
PermissionsStartOnly=true
User=odoo
Group=odoo
ExecStart=/opt/odoo/odoo11-venv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo/odoo11/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo11.conf
StandardOutput=journal+console
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Notify systemd that a new unit file is created and start the Odoo service by executing:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl start odoo11
Check the service status with the following command:
sudo systemctl status odoo11The output should look something like below indicating that Odoo service is active and running.
● odoo11.service - Odoo11
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/odoo11.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2018-01-23 21:09:25 UTC; 1s ago
Main PID: 14146 (python3)
CGroup: /system.slice/odoo11.service
└─14146 /opt/odoo/odoo11-venv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo/odoo11/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo11.conf
Enable the Odoo service to be automatically started at boot time:
sudo systemctl enable odoo11If you want to see the messages logged by the Odoo service you can use the command below:
sudo journalctl -u odoo11Test the Installation
Open your browser and type: http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:8069
Assuming the installation is successful, a screen similar to the following will appear:
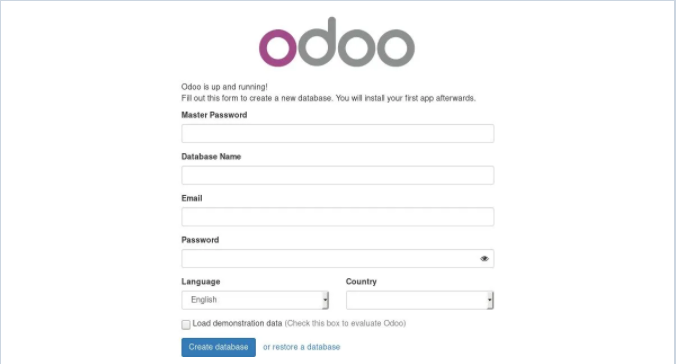
At this point you have a working Odoo 11 installation. You can finish the installation by creating a new database and start working on your project.
Source: https://linuxize.com/post/install-odoo-11-on-ubuntu-16-04/